Being an open source and highly secure CMS, Drupal plays a central role in developing powerful web applications. In fact, many leading brands like Johnson & Johnson, General Electric, eBay, etc., rely on Drupal development to deliver great digital experiences. So, why are industry leaders more inclined to use Drupal to build a web application? Let's find out:
Why should you consider using Drupal to build a web application?
At the time of developing a web application, organizations prefer to use a content management platform that is secure, reliable and flexible. Not only does it allow them to add features as per their choice, but it also allows them to eliminate heavy ones.
As an open source CMS platform, Drupal is trusted by small to large organizations worldwide (such as Nasdaq, Cisco, Tesla and others) to deliver best-in-class digital experiences. Known for its sheer innovation as well as its scalability, Drupal is equipped with a community code that is readily available and a robust architecture tailored to business requirements. Here's why you should consider using Drupal to build a web application in 2022:
Flexibility
Drupal enables you to build exactly the web application you need by offering a powerful framework . It can seamlessly host complex web applications with the help of its core components and APIs. All you need to do is use the right module to get the specific functionality you need. Here are some critical modules to use to build your web application:
Module name | Functionality |
This module plays a key role in defining configuration sets in separate directories at export time and merging them at import time. | |
Whenever a new draft is created, this section offers a tab that reflects all revisions and makes it easy to see all the words that have been added, changed, or deleted. | |
This section enables you to define specific patterns for content at the time it is created. For example, in the case of a blog content type, this section allows you to automatically append /blog to the URL. | |
Enhancing the admin user experience, this section offers a drop-down menu that makes it easy to access the various admin pages. | |
This module simplifies redirect handling in Drupal by automatically creating a redirect for each piece of content with an updated path. |
Whether it's event registrations, detailed analytics, or interactive videos, Drupal has you covered! You can also combine different modules according to your needs. Just like LEGO, Drupal empowers you with a myriad of building blocks that let you build whatever you want.
What makes Drupal flexible?
Drupal is packed with features like creating RSS feeds, managing access rights, aggregating published page entries, commenting on articles and blog posts, etc. Even if these features don't align with your needs, there are more than 48,000 community-contributed modules that Empower Drupal to deliver great plug-and-play functionality in minutes. From gaining information about visitor behavior through Google Analytics to GDPR compliance for cookies, Drupal has a contributor module for everyone!
Customer-centric user experience
Drupal makes it easy for organizations to deliver best-in-class customer-centric experiences. With the right set of tools in place, Drupal empowers organizations to create a web application that meets the needs of visitors and helps them make informed purchasing decisions. The entire interface of the web application is created with customers in mind. By ensuring that interactions are personalized and customer-centric, it aims to deliver a unique experience that is dedicated to fulfilling the specific needs of users throughout their journey.
How does Drupal deliver a customer-centric user experience?
Drupal is enriched with various built-in modules that make it an ideal CMS for the following factors:
Personalization – Drupal comes with several content personalization modules that help provide an experience that is relevant for users. These modules include Personalization Module, Commerce Recommender, Browsing History Recommender and more. While everyone prefers to use a javascript-based client-side solution to implement personalization, there is a lack of contributed modules/frameworks that they sometimes face. Although there is a popular tool called, Acquia Lift that offers enterprise level customization, open source options are few and far between.
Improved Caching Capabilities – When it comes to page loading speed and efficiency, Drupal tops the charts because of its BigPipe and some other caching optimization modules. With the Internal Page Caching module , all page information is cached regardless of whether a user is logged in or not. It makes anonymous visitors experience faster loading of the same content as the page is not started from scratch. Also, the Internal Dynamic Page Cache module is specially designed to cache small portions of each page for each user, regardless of their connection status.
Built-in block system – Rearrange the look and feel of your web application by simply dragging and dropping the required blocks. The same block can be repeated on multiple pages for better design uniformity as well as content reuse.
WYSIWYG Editor – A very useful feature that allows users to preview how the text and images (they've inserted) will look before they even hit the publish button.
Responsive Design – Whether your visitor is accessing your web app via smartphone, desktop or tablet, Drupal's responsive design ensures that it fits perfectly on their screens.
Social Media Modules – Drupal comes with several social media integration modules that make it easy to connect customers to your specific social media channels (Twitter, Facebook, etc.) from your web application.
API-Friendly Architecture
Being a popular support platform for developing various front-end applications, Drupal is known to offer many opportunities for free. Built for today's mediascape, Drupal comes with a first-of-its-kind API initiative that simplifies the process of creating and managing content in one central location. Additionally, it plays a key role in representing multiple front-end versions of this content, each tuned to a specific channel.
What makes Drupal API friendly?
Every modern CMS aims to gain access to powerful APIs and integrate them at every stage of the customer journey for a better experience. The latest versions of Drupal have announced various APIs such as:
RESTful Web Services API - Known to support a disconnected Drupal website. It is responsible for the communication that takes place between native mobile apps and a specific Drupal website. It also takes care of the integration of online services.
JSON:API - By allowing serialization as well as communication via JSON, this module has simplified the process of managing integrations.
Render API - Comes with improved caching protocols and ensures faster page rendering to upgrade the overall user experience.
Translation API - This Drupal API plays a key role in customizing the language in your web application according to the region where your prospect/visitor lives.
Great for SEO
Drupal has been known to be well optimized for search engines since Drupal 7 entered in 2011 with RDF support enabled. According to a Forrester report , semantic structure plays a critical role in streamlining the work of content managers and authors. As Drupal code is semantically written, it leverages alt and title tags for uploaded media (images, charts, etc.) which makes it a popular CMS for SEO.
What makes Drupal search engine friendly?
When it comes to SEO, Drupal can turn anything basic into great with its variety of features like SEO Checklist, XML Sitemap, Global Redirect, SEO Compliance Checker, Metatag Modules, Pathauto and more .
With Drupal's Metatag module , you can easily add meta tags to your web application without any manual effort. This proves to be an advantage for SEO. In fact, this Metatag module enables you to control the appearance of your content on the respective social media channels. Another key aspect that every SEO-friendly web app needs is an intuitive taxonomy system. Drupal is equipped with a flexible classification system that makes it easy to organize content through the use of keywords. Not only does it simplify the organization of information by topic, it also ensures easy navigation in search terms.
Absolute security
Being an open source CMS platform, Drupal's codebase is always carefully controlled. As the code powered by Drupal is freely available for anyone to review, use, modify, as well as contribute, it is imperative to ensure that the code is top notch. Since there are millions of people contributing to this code, it is monitored by a large number of eyes worldwide, which leads to optimal security. In the case of using a closed source CMS platform, there is no clarity about the possible security flaws present in the software. Due to its ability to handle highly critical data, Drupal has been a preferred CMS for web applications built for governments,
Why is Drupal so secure?
To give your web application a high level of security, Drupal comes with a list of various security modules including:
Drupal Login Security – This module enables the administrator to impose several restrictions on user login. Before banning an account, it can limit the total number of invalid login attempts made. It also allows administrators to deny access to specific IP addresses.
Two-Factor Authentication – By leveraging this security module from Drupal, you can get two-factor authentication after a user logs into your application with a specific user ID and password. This involves entering a code received in their email or mobile phone.
Password Policy – This section of Drupal plays a key role in making your login forms more secure, keeping bots and potential security breaches at bay. It imposes various restrictions at the time of setting the password, such as restrictions on character type, length, included case (upper/lower case), etc. It also comes with a password expiration feature that prompts users to change their passwords regularly.
Content Access – This section allows you to gain control over access to content in a granular manner. By defining content types with view, edit or delete rights, you can manage them based on role and author.
Coder – If there are gaps in your code, an attacker is likely to steal your information. Using the Coder module, Drupal code is properly audited to reveal areas where coding practices are not followed correctly.
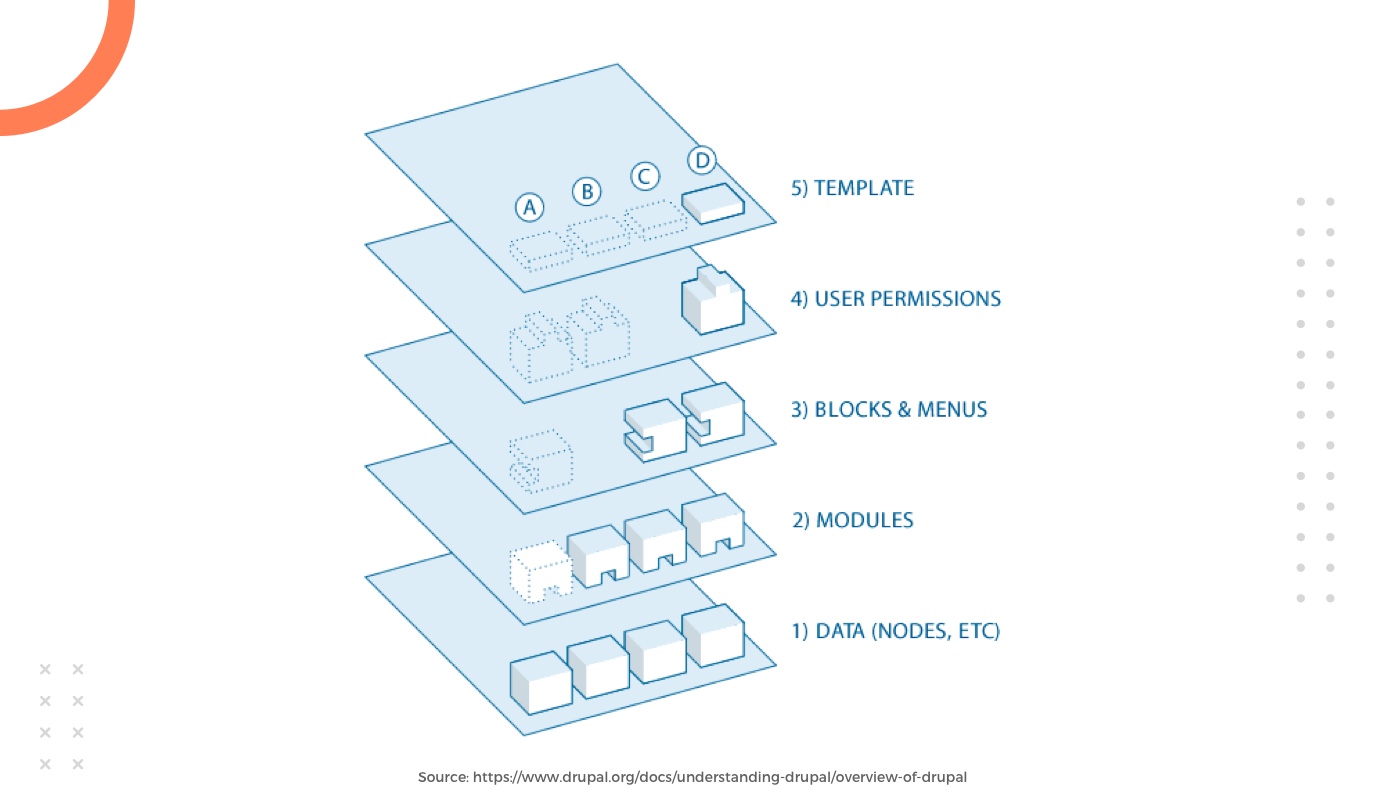
Revealing the Drupal flow
Before you consider Drupal building your web application, it's necessary to take a peek at the layers of the system between which information is passed. Drupal comes with a set of 5 layers, namely:
Data (Nodes, etc.)
Being the foundation of the system, this layer has a collection of all the nodes and is known as the data pool. Everything must be entered as data before it can be displayed in the web application.
Units
The second level in the Drupal flow is modules. Modules can be defined as the functional plugins that are built into the core functionality of Drupal. They can either be a core component of Drupal (when shipped with Drupal) or contributed objects developed specifically by members of the Drupal community. These modules enable you to seamlessly customize data elements to your specific node types, build eCommerce from scratch, sort and display required content programmatically, and more. There are a myriad of options in the ever-evolving repository of Drupal modules that reflect the innovation as well as the collective effort of community members.
Blocks & Menus
The next level in the Drupal flow includes blocks and menus. Blocks are used to get output from a particular module and are mainly created to represent anything you want. These blocks can be placed in many places (called regions) within the template layout you're using, and can be easily configured to output in different ways. Menus are used for navigation in Drupal that help define the content that comes to each corresponding menu path (ie the associated URL). These play a key role in providing links to all the different pages built in Drupal.
User rights
At this stage, settings are configured to control what different users can see and what they are allowed to do. These rights are usually defined based on specific roles which give different users different defined rights.
Role model
This layer contains the site's theme and consists mainly of XHTML and CSS. Due to the mixing of Twig variables, content created in Drupal can easily jump to relevant points. With each theme, there is a defined set of functions that are used to override the standard ones in the mentioned modules. This helps to gain full control over how different modules generate their markups on output.
I think the information shared above is enough for you to understand why you should consider using Drupal to build a web application. As your web application is to be the digital soul of your brand, it must clearly project your business vision and mission. Drupal's leading modular approach and advanced configurations make it easy for businesses to keep pace with the evolving digital landscape.
source: https://www.axelerant.com

Comments